DocumentDB SQL - Operators
An operator is a reserved word or a character used primarily in an SQL WHERE clause to perform operation(s), such as comparisons and arithmetic operations. DocumentDB SQL also supports a variety of scalar expressions. The most commonly used are binary and unary expressions.
The following SQL operators are currently supported and can be used in queries.
SQL Comparison Operators
Following is a list of all the comparison operators available in DocumentDB SQL grammar.
| S.No. |
Operators & Description |
| 1 |
=
Checks if the values of two operands are equal or not. If yes, then condition becomes true. |
| 2 |
!=
Checks if the values of two operands are equal or not. If values are not equal then condition becomes true. |
| 3 |
<>
Checks if the values of two operands are equal or not. If values are not equal then condition becomes true. |
| 4 |
>
Checks if the value of left operand is greater than the value of right operand. If yes, then condition becomes true. |
| 5 |
<
Checks if the value of left operand is less than the value of right operand. If yes, then condition becomes true. |
| 6 |
>=
Checks if the value of left operand is greater than or equal to the value of right operand. If yes, then condition becomes true. |
| 7 |
<=
Checks if the value of left operand is less than or equal to the value of right operand. If yes, then condition becomes true. |
SQL Logical Operators
Following is a list of all the logical operators available in DocumentDB SQL grammar.
| S.No. |
Operators & Description |
| 1 |
AND
The AND operator allows the existence of multiple conditions in an SQL statement's WHERE clause. |
| 2 |
BETWEEN
The BETWEEN operator is used to search for values that are within a set of values, given the minimum value and the maximum value. |
| 3 |
IN
The IN operator is used to compare a value to a list of literal values that have been specified. |
| 4 |
OR
The OR operator is used to combine multiple conditions in an SQL statement's WHERE clause. |
| 5 |
NOT
The NOT operator reverses the meaning of the logical operator with which it is used. For example, NOT EXISTS, NOT BETWEEN, NOT IN, etc. This is a negate operator. |
SQL Arithmetic Operators
Following is a list of all the arithmetic operators available in DocumentDB SQL grammar.
| S.No. |
Operators & Description |
| 1 |
+
Addition − Adds values on either side of the operator. |
| 2 |
-
Subtraction − Subtracts the right hand operand from the left hand operand. |
| 3 |
*
Multiplication − Multiplies values on either side of the operator. |
| 4 |
/
Division − Divides the left hand operand by the right hand operand. |
| 5 |
%
Modulus − Divides the left hand operand by the right hand operand and returns the remainder. |
We will consider the same documents in this example as well. Following is the AndersenFamily document.
{
"id": "AndersenFamily",
"lastName": "Andersen",
"parents": [
{ "firstName": "Thomas", "relationship": "father" },
{ "firstName": "Mary Kay", "relationship": "mother" }
],
"children": [
{
"firstName": "Henriette Thaulow",
"gender": "female",
"grade": 5,
"pets": [ { "givenName": "Fluffy", "type": "Rabbit" } ]
}
],
"location": { "state": "WA", "county": "King", "city": "Seattle" },
"isRegistered": true
}
Following is the SmithFamily document.
{
"id": "SmithFamily",
"parents": [
{ "familyName": "Smith", "givenName": "James" },
{ "familyName": "Curtis", "givenName": "Helen" }
],
"children": [
{
"givenName": "Michelle",
"gender": "female",
"grade": 1
},
{
"givenName": "John",
"gender": "male",
"grade": 7,
"pets": [
{ "givenName": "Tweetie", "type": "Bird" }
]
}
],
"location": {
"state": "NY",
"county": "Queens",
"city": "Forest Hills"
},
"isRegistered": true
}
Following is the WakefieldFamily document.
{
"id": "WakefieldFamily",
"parents": [
{ "familyName": "Wakefield", "givenName": "Robin" },
{ "familyName": "Miller", "givenName": "Ben" }
],
"children": [
{
"familyName": "Merriam",
"givenName": "Jesse",
"gender": "female",
"grade": 6,
"pets": [
{ "givenName": "Charlie Brown", "type": "Dog" },
{ "givenName": "Tiger", "type": "Cat" },
{ "givenName": "Princess", "type": "Cat" }
]
},
{
"familyName": "Miller",
"givenName": "Lisa",
"gender": "female",
"grade": 3,
"pets": [
{ "givenName": "Jake", "type": "Snake" }
]
}
],
"location": { "state": "NY", "county": "Manhattan", "city": "NY" },
"isRegistered": false
}
Let’s take a look at a simple example in which a comparison operator is used in WHERE clause.
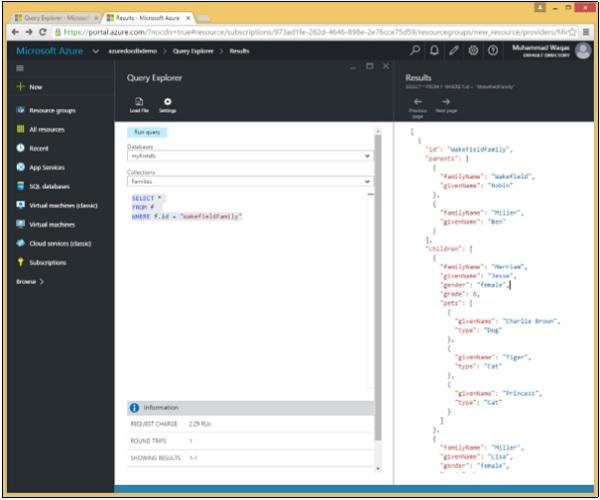
In this query, in WHERE clause, the (WHERE f.id = "WakefieldFamily") condition is specified, and it will retrieve the document whose id is equal to WakefieldFamily.
SELECT *
FROM f
WHERE f.id = "WakefieldFamily"
When the above query is executed, it will return the complete JSON document for WakefieldFamily as shown in the following output.
[
{
"id": "WakefieldFamily",
"parents": [
{
"familyName": "Wakefield",
"givenName": "Robin"
},
{
"familyName": "Miller",
"givenName": "Ben"
}
],
"children": [
{
"familyName": "Merriam",
"givenName": "Jesse",
"gender": "female",
"grade": 6,
"pets": [
{
"givenName": "Charlie Brown",
"type": "Dog"
},
{
"givenName": "Tiger",
"type": "Cat"
},
{
"givenName": "Princess",
"type": "Cat"
}
]
},
{
"familyName": "Miller",
"givenName": "Lisa",
"gender": "female",
"grade": 3,
"pets": [
{
"givenName": "Jake",
"type": "Snake"
}
]
}
],
"location": {
"state": "NY",
"county": "Manhattan",
"city": "NY"
},
"isRegistered": false,
"_rid": "Ic8LAJFujgECAAAAAAAAAA==",
"_ts": 1450541623,
"_self": "dbs/Ic8LAA==/colls/Ic8LAJFujgE=/docs/Ic8LAJFujgECAAAAAAAAAA==/",
"_etag": "\"00000500-0000-0000-0000-567582370000\"",
"_attachments": "attachments/"
}
]
Let’s take a look at another example in which the query will retrieve the children data whose grade is greater than 5.
SELECT *
FROM Families.children[0] c
WHERE (c.grade > 5)
When the above query is executed, it will retrieve the following sub document as shown in the output.
[
{
"familyName": "Merriam",
"givenName": "Jesse",
"gender": "female",
"grade": 6,
"pets": [
{
"givenName": "Charlie Brown",
"type": "Dog"
},
{
"givenName": "Tiger",
"type": "Cat"
},
{
"givenName": "Princess",
"type": "Cat"
}
]
}
]