PyGTK - ComboBox Class
ComboBox is a powerful and popular widget in any GUI toolkit. It provides a dropdown list of items from which a user can choose. The gtk.ComboBox widget implements the CellLayout interface and provides a number of methods to manage the display of items.
The object of gtk.ComboBox class is associated with a ListSore, which is a list model that can be used with widgets that display collection of items. Items are added to ListStore with the append() method. Further, a CellRendererText object is created and packed into the combobox.
Follow these steps to set up a combobox.
combobox = gtk.ComboBox()
store = gtk.ListStore(gobject.TYPE_STRING)
cell = gtk.CellRendererText()
combobox.pack_start(cell)
combobox.add_attribute(cell, 'text', 0)
PyGTK offers a convenience method — gtk.combo_box_new_text() to create a combo box instead of using a list store. Associated convenience methods append_text(), prepend_text(), insert_text() and remove_text() are used to manage the combo boxcontents.
gtk.ComboBox class has the following methods −
| S.NO |
Methods and Description |
| 1 |
set_wrap_width()
Sets the number of columns to be displayed in the popup table layout |
| 2 |
get_active()
Returns the value of the "active" property which is the index in the model of the currently active item |
| 3 |
set_active()
Sets the active item of the combo_box to the item with the model index specified |
| 4 |
set_model()
Sets the model used by the combo box |
| 5 |
append_text()
Appends the string specified by text to the list of strings stored in the combo box list store |
| 6 |
Insert_text()
Inserts the string specified by text in the combo box gtk.ListStore at the index specified by position |
| 7 |
prepend_text()
Prepends the string specified by text to the list of strings stored in the list store |
| 8 |
remove_text()
Removes the string at the index specified by position in the associated liststore |
| 9 |
get_active_text()
Returns the currently active string |
The ComboBox widget emits the following signals −
| changed |
This is emitted when a new item in the combo box is selected |
| move_active |
This is a keybinding signal which gets emitted to move the active selection. |
| Popdown |
This is a keybinding signal which gets emitted to popdown the combo box list. The default bindings for this signal are Alt+Up and Escape |
| Popup |
This is a keybinding signal which gets emitted to popup the combo box list. The default bindings for this signal are Alt+Down. |
Two example codes for the demonstration of ComboBox are given below.
Example 1
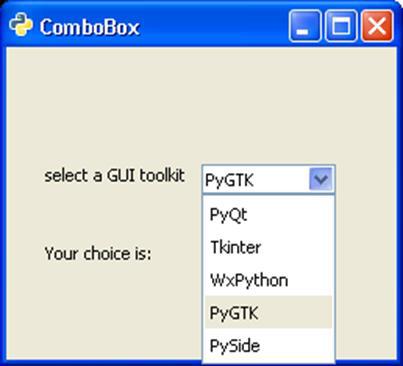
In this example, a ListStore is populated with the names of popular Python GUI toolkits and it is associated with a ComboBox widget. As a user makes a choice, the changed signal is emitted. It is connected to a callback function to display the user's choice.
import pygtk
pygtk.require('2.0')
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("ComboBox with ListStore")
self.set_default_size(250, 200)
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
combobox = gtk.ComboBox()
store = gtk.ListStore(str)
cell = gtk.CellRendererText()
combobox.pack_start(cell)
combobox.add_attribute(cell, 'text', 0)
fixed = gtk.Fixed()
lbl = gtk.Label("select a GUI toolkit")
fixed.put(lbl, 25,75)
fixed.put(combobox, 125,75)
lbl2 = gtk.Label("Your choice is:")
fixed.put(lbl2, 25,125)
self.label = gtk.Label("")
fixed.put(self.label, 125,125)
self.add(fixed)
store.append (["PyQt"])
store.append (["Tkinter"])
store.append (["WxPython"])
store.append (["PyGTK"])
store.append (["PySide"])
combobox.set_model(store)
combobox.connect('changed', self.on_changed)
combobox.set_active(0)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
return
def on_changed(self, widget):
self.label.set_label(widget.get_active_text())
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
PyApp()
gtk.main()
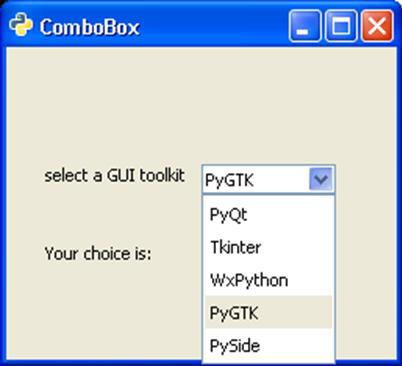
Upon execution, the program displays the following output −
Example 2
The second version of the program uses the convenience method combo_box_new_text() to create a combo box and append_text() function to add strings in it. In both programs, the get_active_text() method is used to fetch user's selection and display on a label on the window.
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Simple ComboBox")
self.set_default_size(250, 200)
self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER)
cb = gtk.combo_box_new_text()
cb.connect("changed", self.on_changed)
cb.append_text('PyQt')
cb.append_text('Tkinter')
cb.append_text('WxPython')
cb.append_text('PyGTK')
cb.append_text('PySide')
fixed = gtk.Fixed()
lbl = gtk.Label("select a GUI toolkit")
fixed.put(lbl, 25,75)
fixed.put(cb, 125,75)
lbl2 = gtk.Label("Your choice is:")
fixed.put(lbl2, 25,125)
self.label = gtk.Label("")
fixed.put(self.label, 125,125)
self.add(fixed)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
def on_changed(self, widget):
self.label.set_label(widget.get_active_text())
if __name__ == '__main__':
PyApp()
gtk.main()
The output of this program is similar to that of the previous program.