Watir - Locating Web Elements
In Watir for testing, you need to locate the elements and it can be done in different ways – by using the id, class or text of the element.
In this chapter, we will see few examples which shows different ways to locate elements.
Using ID of the Element
Test page
<html>
<head>
<title>Testing UI using Watir</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function wsentered() {
console.log("inside wsentered");
var firstname = document.getElementById("firstname");
if (firstname.value != "") {
document.getElementById("displayfirstname").innerHTML =
"The name entered is : " + firstname.value;
document.getElementById("displayfirstname").style.display = "";
}
}
</script>
<div id = "divfirstname">
Enter First Name :
<input type = "text" id = "firstname" name = "firstname" onchange = "wsentered()" />
</div>
<br/>
<br/>
<div style = "display:none;" id = "displayfirstname">
</div>
</body>
</html>
Example
require 'watir'
b = Watir::Browser.new :chrome
b.goto('http://localhost/uitesting/textbox.html')
t = b.text_field(id: 'firstname') // using the id of the textbox to locate the textbox
t.exists?
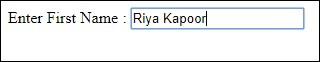
t.set 'Riya Kapoor'
b.screenshot.save 'textboxbefore.png'
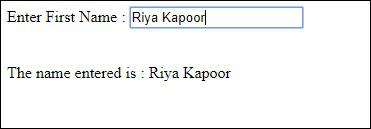
t.value
t.fire_event('onchange')
b.screenshot.save 'textboxafter.png'
In this example, we are using id of the textbox element to locate it and set the value.
t = b.text_field(id: 'firstname')
Output
In case you need to locate the div, span or any other html tag you can do same using id as follows −
For div
browser.div(id: "divid")
browser.div(id: /divid/)
For span
browser.span(id: "spanid")
browser.span(id: /spanid/)
Using NAME of the Element
Test page
<html>
<head>
<title>Testing UI using Watir</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type = "text/javascript">
function wsentered() {
console.log("inside wsentered");
var firstname = document.getElementById("firstname");
if (firstname.value != "") {
document.getElementById("displayfirstname").innerHTML =
"The name entered is : " + firstname.value;
document.getElementById("displayfirstname").style.display = "";
}
}
</script>
<div id = "divfirstname">
Enter First Name :
<input type = "text" id = "firstname" name = "firstname" onchange = "wsentered()" />
</div>
<br/>
<br/>
<div style = "display:none;" id = "displayfirstname">
</div>
</body>
</html>
Example
require 'watir'
b = Watir::Browser.new :chrome
b.goto('http://localhost/uitesting/textbox.html')
t = b.text_field(name: 'firstname') // name is used to locate the textbox element
t.exists?
t.set 'Riya Kapoor'
b.screenshot.save 'textboxbefore.png'
t.value
t.fire_event('onchange')
b.screenshot.save 'textboxafter.png'
Output


Using Tag Name
You can locate any html elements you want by directly using the html tag as shown below.
For div
browser.div(id: "divid")
browser.div(id: /divid/)
For span
browser.span(id: "spanid")
browser.span(id: /spanid/)
For p tag
browser.p(id: "ptag")
browser.p(id: /ptag/)
For button
browser.button(id: "btnid")
browser.button(id: /btnid/)
Using Class Name
You can locate the element using its classname. It can be done as shown below −
For div
browser.div(class: "divclassname")
browser.div(class: /divclassname/)
For span
browser.span(class: "spanclassname”)
browser.span(class: /spanclassname/)
For p tag
browser.p(class: "pclassname")
browser.p(class: /pclassname/)
For button
browser.button(class: "btnclassname")
browser.button(class: /btnclassname/)
For textbox
browser.text_field(class: 'txtclassname')
browser.text_field(class: /txtclassname/)
You can also pass multiple classes as shown below −
For div
browser.div(class: ["class1", "class2"])
Using Text
This is yet another way to locate elements by using elements with a text. For example −
browser.button(text: "button text")
browser.button(text: /button text/)
Using Label
You can use the label of the element to locate it as shown below −
browser.text_field(label: "text here"))
browser.text_field(label: /text here/))
Using Data Attributes
In-case you have data attributes to your html tags, you can locate the elements using it as shown below −
For example, you can locate the tag as shown below −
<div data-type = "test1"></div>
You can locate the div as follows −
browser.div(data-type: 'test1'))
browser.div(data-type: /test1/))
Using Custom Attributes
You can also locate the elements using custom attributes as shown below −
Example of html element
<div itemprop = ”content”>
….
</div>
You can locate the div as follows −
browser.div(itemprop: ‘content'))
browser.div(itemprop: /content/))
Using Visible Attribute
The element using visible attribute can be located as shown below −
browser.div(visible: true)
browser.div(visible: false)